In today's digital landscape, online security has become paramount. Users expect their personal information to be handled safely when browsing websites. One common issue that compromises this safety is the lack of HTTPS, an encrypted connection protocol. In this blog, we will explore the No HTTPS problem and its potential consequences, along with the solution to enhance your website's security.
We also provide website optimization service. Contact ALSA IT

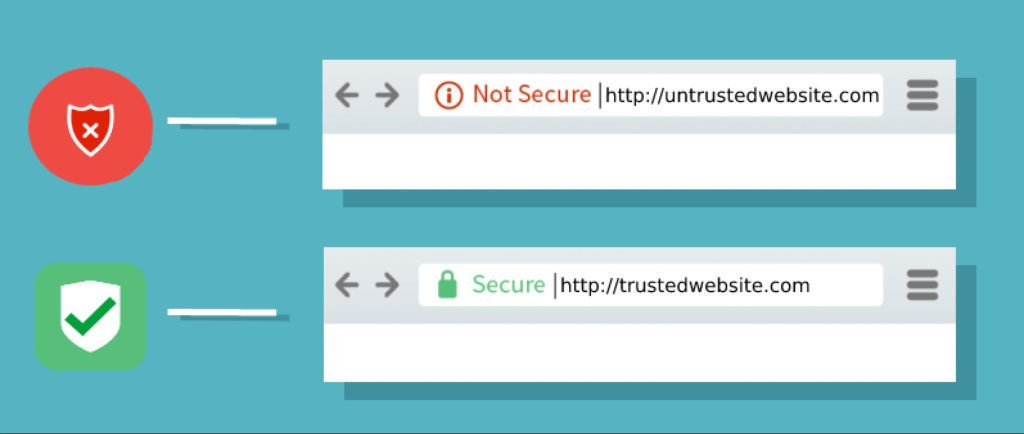
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the protocol used for transmitting data between a website and its visitors' browsers. However, HTTP alone doesn't provide encryption, leaving data vulnerable to interception by attackers. No HTTPS refers to websites that still rely solely on HTTP, without the added security of HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure).
Consequences of No HTTPS:
Data Interception: Without HTTPS, any data transmitted between the website and user can be easily intercepted by hackers. This includes personal information, login credentials, payment details, or any other sensitive data shared on the website.
Privacy Concerns: Lack of HTTPS also poses privacy issues. Third-party entities, such as Internet Service Providers (ISPs) or government agencies, can track users' activities on non-secure websites, compromising privacy rights.
Loss of User Trust: In an era where cyber attacks are commonplace, users have become more cautious. Websites without HTTPS indicators, such as the lock symbol in the browser's address bar, can be seen as untrustworthy, resulting in decreased user confidence and potential loss of business.

Fortunately, rectifying the No HTTPS problem involves adopting HTTPS to establish secure connections. Here's how you can implement this crucial security measure:
The No HTTPS problem poses risks to user data, privacy, and overall trust in your website. By implementing HTTPS, you can ensure secure connections and protect sensitive information. Investing in an SSL certificate and redirecting HTTP traffic to HTTPS not only mitigates potential security threats but also helps build trust with users. Stay ahead in the digital era by prioritizing online security with HTTPS implementation for your website.
We also provide website optimization service. Contact ALSA IT